Abstract
We have completed a phase 1 trial in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with the novel RNA-directed nucleoside analog 8-chloro-adenosine (8CA), demonstrating clinical activity (NCT02509546). Our pre-clinical data suggest that 8CA synergizes with the BCL2-inhibitor Venetoclax (VEN) in AML, thus providing the basis for our next therapeutic study.
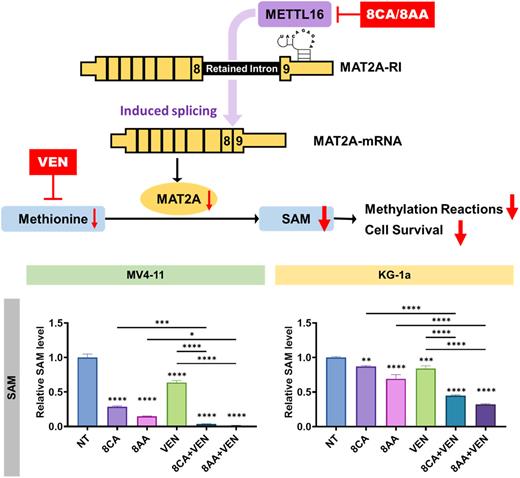
Targeting the metabolic dependencies of cancer cells is a promising strategy. A recent integrated genomic-metabolic profiling study has revealed that the cysteine and methionine metabolism is one of the most significantly altered metabolic pathways in AML blasts in contrast to healthy blood cells. The essential amino acid methionine is converted by the rate-limiting enzyme methionine-adenosyltransferase-2A (MAT2A) into S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM), which is the principle global methyl-donor for methylation reactions regulating gene expression. To maintain SAM homeostasis, MAT2A expression is elegantly regulated by the dwell-time of RNA methyltransferase METTL16 on MAT2A RNA: when adequate SAM levels are present, METTL16 utilizes SAM to methylate the hairpin structure of MAT2A RNA in a brief time and then leaves intron-retained MAT2A RNA alone for degradation; when SAM levels are depleted, this methylation step is impaired due to insufficient enzymatic turnover, prolonging the occupancy time of METTL16 on the hairpin structure, which then drives the splicing of MAT2A RNA to produce functional MAT2A protein for increased SAM biosynthesis.
Through mass spectrometry, we found that VEN, which is approved by the FDA for AML treatment, decreases cellular uptake of methionine, but subsequently up-regulates the cysteine and methionine metabolism pathway in AML cell lines MV4-11 and KG-1a, which suggests a compensatory mechanism. Meanwhile, our novel anti-cancer nucleoside analogs 8CA and 8-amino-adenosine (8AA) significantly suppress the cysteine and methionine metabolism pathway in the two cell lines; importantly, among all genes investigated in this pathway, the MAT2A gene was downregulated the most. Through western blotting and qRT-PCR, we found that 8CA/8AA impair the splicing of MAT2A RNA and decrease MAT2A protein level in MV4-11 and KG-1a cells in a dose-dependent manner, which is mediated through inhibition of METTL16 protein stability. Importantly, through flow cytometry analysis, we found 8CA/8AA suppress protein expression of MAT2A and METTL16 in CD34+CD38- leukemia stem cells (LSCs) isolated from the bone marrow of patients with AML. Also, we observed that 8CA/8AA significantly downregulate both SAM and histone methylation levels in MV4-11 and KG-1a cells, and that downregulation of SAM and histone methylation is augmented when 8CA/8AA are used in combination with VEN. Moreover, 8CA/8AA synergize with VEN in inhibiting the proliferation of AML cell lines and primary AML blasts.
In summary, our findings demonstrate that 8CA/8AA synergize with VEN in targeting AML through disrupting the methionine-MAT2A-SAM axis and suggest the combination of 8CA/8AA and VEN is a promising novel therapeutic regimen for treatment of AML.
Figure.Top: 8CA/8AA accelerate the degradation of METTL16 protein, which is required for the successful splicing of MAT2A RNA, and consequently decrease MAT2A protein level and thereby synergize with VEN in inhibiting the Methionine-MAT2A-SAM axis to target AML cell lines (MV4-11, KG-1a) and LSCs. Bottom: MV4-11 and KG-1a were treated with vehicle (not treated, NT), 1 μM 8CA/8AA in complete media for 48 h and the intracellular SAM and SAH levels were measured through mass spectrometry (n=3). nsp ≥ 0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments, are shown as mean ± SD, and are compared among multiple groups by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Disclosures
Rosen:January Therapeutics: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal